News
VS Code Dev Intros Open Source Markdown Language Server
A member of Microsoft's Visual Studio Code development team this week introduced the culmination of a six-month pet project: a Markdown Language Server.
Matt Bierner, a maintainer of JavaScript/TypeScript for the VS Code team, has completely changed the way Markdown works in the editor, replacing (and adding to) functionality that was previously baked into the editor and augmented by Markdown extensions.
Markdown, to review, is a lightweight markup language for creating formatted text using a plain-text editor. Markdown files with an .md file extension are commonly used in GitHub to provide descriptions of projects in README.md files.
His novel idea was to provide Markdown functionality via a language server that he had to create from scratch. Such language servers -- following the Language Server Protocol -- are commonly used in code editors/IDEs to provide language-specific "smarts" such as auto complete, go to definition, documentation on hover, error-checking (diagnostics), find all references and much more.
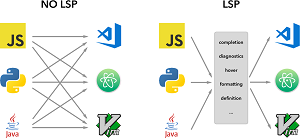 [Click on image for larger view.] Language Server vs. No Language Server (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] Language Server vs. No Language Server (source: Microsoft).
To that end, he created the Markdown Language Service -- a TypeScript library that provides tools for working with Markdown -- and the Markdown Language Server, built using that Markdown Language Service.
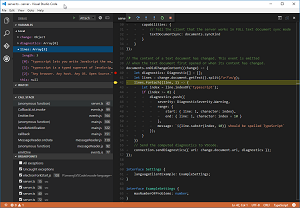 [Click on image for larger view.] Using a Language Server in Debugging (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] Using a Language Server in Debugging (source: Microsoft).
This approach brings multiple benefits. For one thing, Markdown tooling runs as a separate executable, so using Markdown won't block other extensions that previously had to vie for process time as they all leveraged normal extension APIs. While measured in milliseconds, such delays can be bothersome.
More important, Markdown functionality becomes portable.
"With this language server, we're making most of VS Code's built-in Markdown language tooling -- everything from document outlines, to smart folding, to path completions -- available to other editors and tools," Bierner said in an Aug. 16 blog post. While portability to other editors is a primary benefit, the project's GitHub repo warns that the language server is still in development and hasn't been tested with other clients.
Bierner's effort required an exhaustive, incremental approach over many months, sparked by the frustration of having to manually type out and verify clickable links. Starting with link completion functionality, he removed more and more code from the team's Markdown extension and put it into his pet project.
Now, the set of Markdown language features includes:
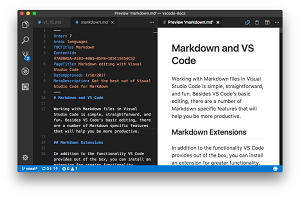 [Click on image for larger view.] Markdown Preview Github Styling Extension (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] Markdown Preview Github Styling Extension (source: Microsoft).
Since joining the VS Code team in 2016 and taking ownership of Markdown support, Bierner has been active in creating extensions -- at least 20 -- including the Markdown Preview Github Styling tool, which has been installed nearly 760,000 times (pictured in above graphic).
"In many ways, the past six months have seen more advances in VS Code's Markdown tooling than the past six years I've been working in the space," Bierner said. "Today we are shipping many new tools, some of which have not been available for Markdown before. Many of these features benefit the most casual readers and writers of Markdown, while others will only be appreciated by advanced users. However for all this progress, I know that we've only just started to explore what's possible in Markdown tooling.
"What really gets me excited about the Markdown Language Server is that now the project is bigger than just VS Code. By making our Markdown tooling easy to consume, my hope is that we can help push Markdown tooling forward for everyone. These open source projects are invitations to help build the future of Markdown tooling together."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.