News
Low-Code Power Apps Uses AI for No-Code Natural Language Development: 'The Code Writes Itself'
Microsoft's low-code Power Apps is seemingly headed to no-code, helping developers leverage AI to create applications with natural language.
That breakthrough, of course, is eagerly awaited by enterprises and their "ordinary business users" who could conceivably take over development chores from hard-to-find and expensive professional coders. It's so important that Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella mentioned it some six minutes into in his opening keynote address for last week's Build 2021 developer conference. "We are bringing the world's most powerful language model, GPT-3, to Power Platform," he said. "If you can describe what you want to do in natural language, GPT-3 will generate a list of the most relevant formulas for you to choose from. The code writes itself."
That language model comes from OpenAI, an AI research and deployment company.
"Given any text prompt like a phrase or a sentence, GPT-3 returns a text completion in natural language," the company says. "Developers 'can program' GPT-3 by showing it just a few examples or 'prompts.' We've designed the API to be both simple for anyone to use but also flexible enough to make machine learning teams more productive."
That flexibility is being leveraged in Power Apps, part of Microsoft's Power Platform.
Microsoft fine-tuned GPT-3 to automatically generate Power Fx formulas based on natural language input, Microsoft's Ryan Cunningham, Director PM, Power Apps, said in a blog post last week. "We're adding GPT-3 and other Microsoft AI technology directly into Power Apps Studio in a way that will help every maker quickly build the apps they need and more easily learn advanced concepts in the process."
 [Click on image for larger, animated GIF view.] GPT-3 in Animated Action (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger, animated GIF view.] GPT-3 in Animated Action (source: Microsoft).
Power Fx is described as a general-purpose, strongly typed, declarative and functional programming language that helps users create canvas-based apps as opposed to model-based apps, as we explained earlier this year.
The project's GitHub site indicates the language -- based on Excel-like formulas for working with data in spreadsheets -- originated with the canvas-app functionality provided in Power Apps. "We are in the process of extracting the language from that product so that we can use it in more Microsoft Power Platform products and make it available here for you to use," Microsoft said.
 [Click on image for larger view.] What Is Power Fx? (source: Rory Neary).
[Click on image for larger view.] What Is Power Fx? (source: Rory Neary).
Cunningham shed more light on the project last week. "Now you'll be able to simply tell Power Apps what you'd like to see -- for example, 'show me customers from the US whose subscription expired' -- and a set of formulas will be presented along with an explanation of how they work. Simply select one to apply the logic to your app."
He also explained another Power Apps feature: Programming by examples (PBE), an industry paradigm that Microsoft has been interested in for years. It seeks to teach new behavior to a computer by demonstrating actions on concrete examples. Cunningham explained how this new frontier in AI can empower users to create scripts from input-output examples.
"AI powered PBE empowers users to easily manage and manipulate data within galleries and data tables, by applying patterns or formula on the original value. Instead of applying a complex formula, users can program the model by showing it examples. If data is well formatted, one example may be enough to program it. If not, users can program the model with more examples."
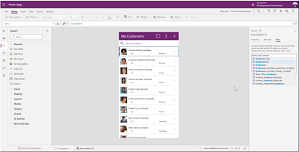
The following graphic illustrates an example scenario in which an e-commerce vendor modifies customer names presented in a data table, changing the first name and last name to the first name and the initial of the last name, for example: "John Smith" to "John S."
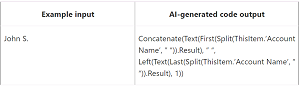 [Click on image for larger view.] PBE Example (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] PBE Example (source: Microsoft).
"The ultimate low-code app building experience is one where you describe in plain language what you want an app to do, and in an instant that app is created for you," Cunningham said. "Today we're taking a major step toward that dream."
Who knows? Someday this reporter might be able to talk into a microphone to create content like this: "Write me an article on how Power Apps is using AI technology to further natural language development."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.