News
Top .NET Vulnerabilities: SQL Injection, Path Traversal and Cross-Site Scripting, Says Security Firm
Contrast Security published an analysis of real-world application attack and vulnerability data from September 2019, finding that in the .NET world, the top three vulnerabilities were SQL Injection, Path Traversal and Cross-Site Scripting, followed by XML External Entity Injection (XXE) and Xpath Injection.
That list speaks to a broader pattern, said the AppSec Intelligence report, which the company said is used by developers and others to better understand application security threats, adjust security controls and improve their security posture. It said Cross-Site Scripting, XML External Entity Injection and Cross-Site Request Forgery were the most prevalent vulnerabilities across the board, while, for the second month in a row, the most common attack types were SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and Path Traversal.
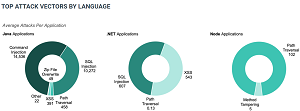 [Click on image for larger view.] Top Attack Vectors by Language (source: Contrast Security).
[Click on image for larger view.] Top Attack Vectors by Language (source: Contrast Security).
The firm listed this summary for the September report, published today (Oct. 22):
-
Custom Code Vulnerabilities: Applications had an average of 6 open, serious vulnerabilities in September.
-
Top Vulnerabilities by Language: Injection vulnerabilities dominated in September. Cross-Site Scripting is the most prevalent serious vulnerability for Java applications and in the top three for .NET and Node applications. SQL Injection and Command Injection vulnerabilities are the most common for .NET and Node applications, respectively.
-
Custom Code Attacks: We saw the continued dominance of attacks on custom code, making up 99 percent of attacks. The top attacks on CVEs were CVE-2017-5638, CVE-2010-4467, and CVE-2017-9791. SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting, and Path Traversal attacks, the top attacks on custom code, each targeted 55 percent of applications.
-
Top Attack Vectors by Language: Injection attacks continued to dominate, with Java applications targeted the highest number of Command Injection attacks and .NET applications targeted by the highest number of SQL injection attacks.
- Geo Location: Attacks originated across the globe in September, with the most attacks originating from North America, specifically the United States. India and the Netherlands were the next most common origin countries.
Contrast Security's latest monthly analysis revealed a 40 percent increase in total attacks compared to August, equaling the level of July, with 1 percent of those attacks connected to a vulnerability within an application, which is a .7 percent decrease from last month. "The other 99 percent were probes and did not connect with a corresponding vulnerability within the target application -- a striking fact for security teams using tools that cannot distinguish between ineffective and effective attacks!" the company said.
More information can be found in today's blog post.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.