News
After Lagging .NET 5 Support, What's Next for Azure Functions?
Microsoft this month announced its Azure Functions -- for serverless cloud computing -- now supports .NET 5, an umbrella offering that followed the .NET Core series of open source, cross-platform releases, which supplanted the old .NET Framework.
.NET 5 debuted in November 2020, and most of the .NET ecosystem -- including third-party vendors -- has already jumped on the support bandwagon, with Microsoft admitting Azure Functions is late in that regard. For example, Azure Functions 3.0 reached general availability with support for .NET Core 3.1 in late January.
Because tight coupling between the Azure Functions runtime and .NET caused synchronization issues with the .NET lifecycle that dictates Long-Term Support (LTS) intermixed with "Current" (non-LTS) releases, the Azure Functions dev team had to shift gears to add support for the Current .NET 5 release (.NET 6 will be LTS).
"To enable .NET 5 in Azure Functions, we are moving to an out-of-process model that runs a .NET 5 worker process alongside the runtime," said the team's Anthony Chu, in a blog post that was updated earlier this month. "This is the same out-of-process model that all non-.NET Azure Functions languages have used successfully since Azure Functions V2."
The Azure Functions .NET Worker GitHub repo says the project introduces an Isolated Model for that scheme, allowing developers to have full control over an application's dependencies as well as other new features such as a middleware pipeline. Such benefits, however, are counterbalanced by missing features that were available in previous Azure Functions versions, such as Durable Functions and support for rich types.
The new model was long in coming, but things will get synchronized with the .NET lifecycle in November with the LTS .NET 6 GA release, allowing for much quicker support of new .NET versions. Because the worker comes as a NuGet package, developers can update the .NET version when .NET 6 comes out and stay on the new out-of-process worker model or use the older in-process model.
"We realize that customers who are early adopters of .NET 5 have been disappointed by the delay of .NET 5 in Azure Functions," Chu said. "Building a new language worker from scratch has taken some time. We understand your frustration and appreciate your patience. The investment to separate the .NET worker from the runtime will allow us to quickly support future .NET versions. We expect to support .NET 6 LTS as soon as it is released."
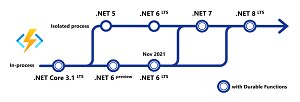 [Click on image for larger view.] Future of .NET on Azure Functions (source: Microsoft).
[Click on image for larger view.] Future of .NET on Azure Functions (source: Microsoft).
Chu also posted a roadmap indicating what's coming up for Azure Functions, with parts of it reading (verbatim):
- .NET 6 LTS: .NET 6 functions will support both in-process and isolated process options. The in-process option will support the full feature set available in .NET Core 3.1 functions today, including Durable Functions and rich binding types. The isolated process option will provide an upgrade path for apps using this option for .NET 5 and initially will have the same feature set and limitations.
-
.NET 7 and Beyond: Long term, our vision is to have full feature parity out of process, bringing many of the features that are currently exclusive to the in-process model to the isolated model. We plan to begin delivering improvements to the isolated model after the .NET 6 general availability release.
.NET 7 is scheduled for the second half of 2022, and we plan to support .NET 7 on day 1 exclusively in the isolated model. We expect that you'll be able to migrate and run almost any .NET serverless workload in the isolated worker -- including Durable Functions and other targeted improvements to the isolated model.
- .NET Framework: Currently, .NET Framework is supported in the Azure Functions V1 host. As the isolated model for .NET continues to evolve, we will investigate the feasibility of running the .NET isolated worker SDK in .NET Framework apps. This could allow users to develop apps targeting .NET Framework on newer versions of the functions runtime.
Developers can learn more in an Azure Functions Live - Mar 2021 - .NET Roadmap webcast being held tomorrow, March 25.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.